People With Antisocial Behavior May Have A Different Brain Structure

The University College London (UCL) conducted research on the human brain that the journal Lancet published in the February 2020 in its section on psychiatry. The article studies the association between antisocial behavior and brain structure.
This research was carried out in collaboration between the London institution and researchers from New Zealand, where the individuals studied came from. In New Zealand, the institution that provided the study subjects was the Queen Mary Hospital .
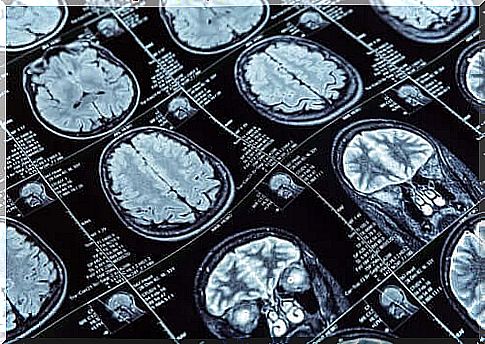
To further the research, a nuclear magnetic resonance was performed on more than 600 people aged 45 years at the time of the imaging test. These 600 people are part of a larger group of more than a thousand that New Zealanders have monitored since childhood.
What is intended to be determined are the factors that can influence, throughout life, that someone develops antisocial behaviors or habits. If these factors are detected, it would be possible to influence them to prevent crimes, for example.
In the MRIs carried out on the research participants, the thickness of the cerebral cortex and the amount of gray matter they had were measured. These data would allow a comparison between those with antisocial behaviors and those who do not.
What and who is classified as antisocial?
What do we mean by antisocial behavior? It is a difficult concept to define as it varies according to the age and culture of those involved. What is considered antisocial in Europe is not the same as in Asia.
Antisocial behavior can be defined as behavior performed by someone that is contrary to the interests of society . It is a way of being and acting that violates the norms established by the majority.
The range of antisocial acts is wide. We can range from traffic violations to robberies committed with notorious violence. Adolescents’ addictive practices also fall into this category, such as alcohol consumption.
Second, antisocial behavior can be personality traits of a person who rebels against an authority, which can be their parents or the law itself. Behavior was also understood as a challenge in relation to institutions.
There need not necessarily be a pathology that accompanies antisocial behaviors. Most of the time, it is just a way of acting that does not qualify for any psychiatric clinical picture.
Anyway, the science has established the existence of something called antisocial personality disorder. They are people who repeatedly break the rules, who are impulsive and who do not regret their acts of transgression. This diagnosis only applies to people over 18 years of age.
Search results
Research published in the journal Lancet reveals that, to complete the study, the participants were divided into three groups :
- 80 people with a history of antisocial problems;
- 151 people with an antisocial history limited to the period of adolescence;
- 441 people with no records of antisocial behavior prior to this stage of life.
Significant results were found in the first group. The brain MRIs of these people showed a shrinkage of the cerebral cortex compared to the others, as well as a slightly smaller amount of gray matter.
On the other hand, in the group with antisocial problems in adolescence and in those without a history, there were no differences. This reveals that certain behaviors from an early age can be explained more culturally than biologically .
What is evident is the change in brain architecture that a small group of the population can have in relation to antisocial behaviors. These changes could explain the antisocial personality that persists over the years.

Previous Studies on Antisocial Behavior and the Brain
The results published in the Lancet add to a series of previous research on the same subject. Different universities worked on the topic at different ages and in different countries.
Adolescents with antisocial problems, for example, have already been shown to have alterations in the frontal and temporal regions of the brain. Furthermore, with more serious connotations, violent prisoners in prisons have less gray matter.
Specifically, the researchers were looking at the emotional region of the brain to find some association. Assuming that antisocial problems are characterized by a lack of empathy, it was logical to look for changes in this place. The results indicated that antisocial teenagers had smaller cerebral amygdala, and the amygdala is the seat of empathy.
We can conclude that this new research confirms that the anti-social problems have a certain relationship with the structure and architecture of the brain, and these changes are another factor that determines antisocial behavior throughout life.