How To Differentiate A Herniated Disc From A Back Pain
There are several types of back pain, which vary in duration and intensity. Unfortunately, they have become more and more common over the years and the hectic and stressful day-to-day life that most people experience today. Today we’ll talk about differentiating between a herniated disc and back pain.
The pain we feel in the back is usually mild and disappears after a while, when we exercise, stretch, massage, or simply rest for a while.
However, there are situations in which these pains last longer, and can even be a warning of the body regarding more serious conditions that need to be treated.
When it comes to something that has become so common and commonplace, how do you know when it’s really a simple back pain and when we’re dealing with a more serious condition like a herniated disc?
What is a herniated disc?
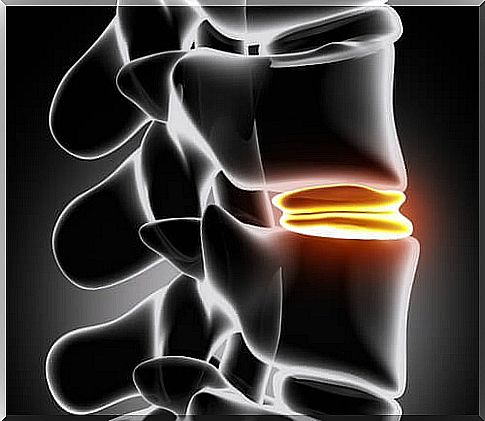
This condition refers to a problem with one or both discs present in the back, which are like pillows located between the vertebrae. These discs have a gelatinous interior and a more rigid exterior.
However, in some situations, the exterior of the same can break, allowing a part of the “gelatin” present internally to come out through the cracked area. This situation can irritate the nerves in the area and cause pain.
Disc herniation usually occurs in the lumbar or cervical region, as these are areas that are more exposed to movement and that suffer more from some of our actions.
These are some of the main causes of herniated disc:
- Excessive pressure on the affected region, which can be caused by sudden movements or even strong sneezing.
- Activities performed frequently and repetitively, such as lifting weights incorrectly, for example.
- Exercise or sports related injuries.
- Gradual, age-related wear, which causes discs to become less flexible and more prone to breakage, even with subtler movements.
Differences between herniated disc and back pain

First, it is important to emphasize that the herniated disc does not always present clear symptoms that allow it to be identified.
A person can have a herniated disc and not feel pain, and therefore not know that there is something wrong with their body.
As mentioned, pain can occur in the lower back, or in the cervical region, although the latter case is less frequent.
Since the main symptom is pain, it is easy to confuse a herniated disc at first with a simple back pain. One way to differentiate them is due to their intensity and duration.
A pain in the back usually goes away after a while if we relax and allow ourselves to rest.
Hernias, on the other hand, can continue to cause pain for a longer period of time, in addition to increasing the intensity little by little.
Although this may be a good indicator, the key point to clarify the difference between these two conditions is the fact that a herniated disc affects the nerves, and therefore the pain resulting from it has some different aspects:
- Pains in arms or legs. If the hernia is in the cervical region, the pain may extend to the arms; if it’s in the lower back, the pain can radiate to the buttocks, thighs, and even calves.
- Increased pain when coughing and sneezing.
- Numbness and tingling. This can occur in areas controlled by the nerves affected by the hernia.
- Weakness. The muscles that are served by the affected nerves can weaken, reducing our ability to lift and hold heavy items, or even walk and run as we did before.
What to do when identifying the symptoms of a herniated disc?
If you suspect that your back pain may actually be characteristic of a herniated disc, it is very important to consult a doctor, as only he or she will be able to provide the correct diagnosis and prescribe the best treatment options.
Treatment for herniated discs can involve different therapies, including traditional pain relieving medications, specific nerve pain medications, muscle relaxants, cortisone injections, physiotherapy and even surgery, although the latter is needed in a very small number. of cases.
Anyway, only your doctor can indicate the best solution for your case. For this reason, be aware of symptoms and seek medical attention as soon as possible.